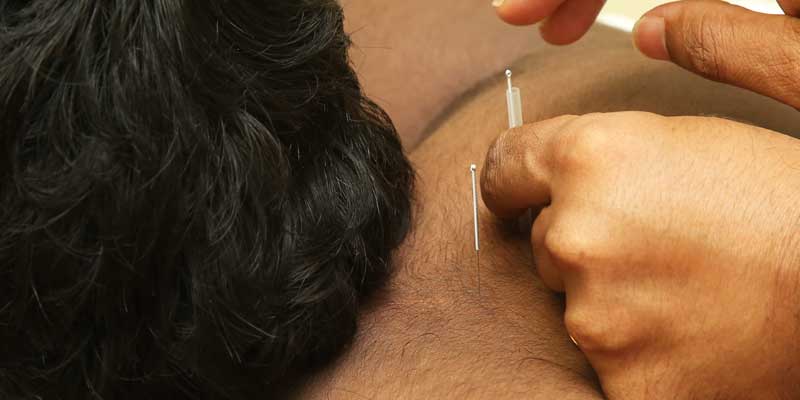
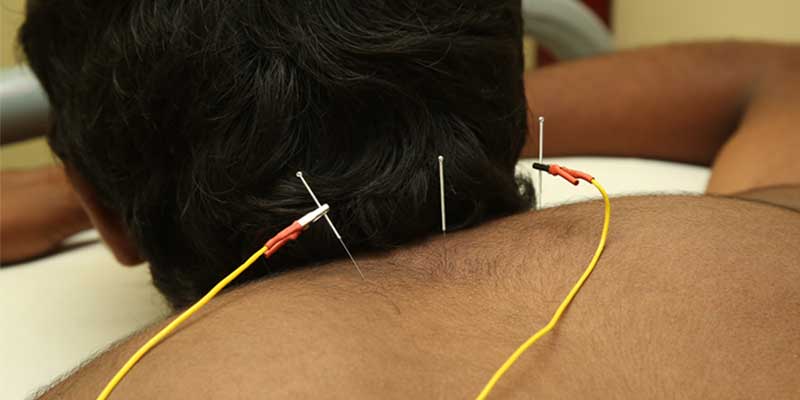
ACUPUNCTURE
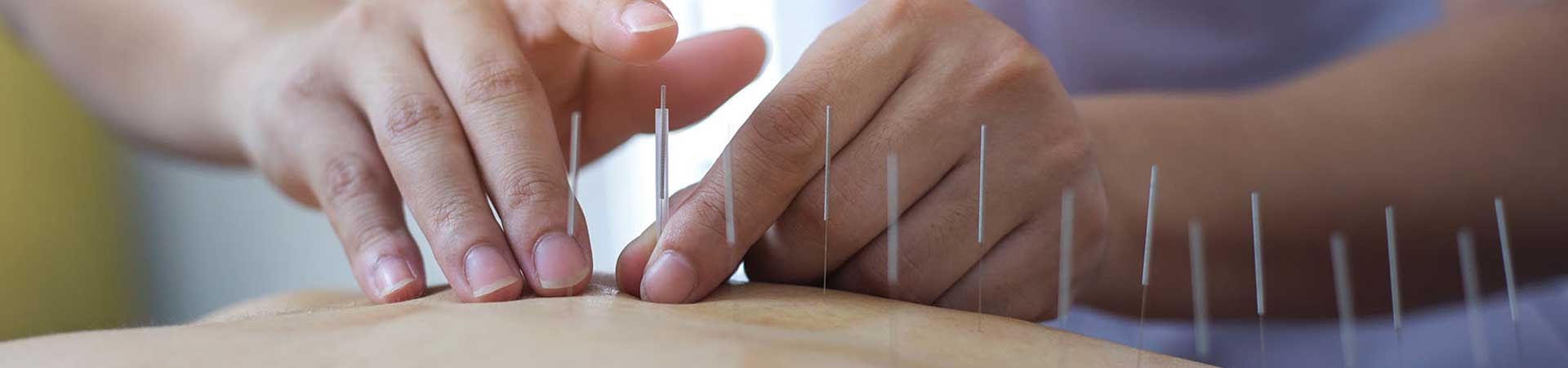
Acupuncture is the most ancient therapeutic technique of Chinese Medicine. It is most valuable in both acute and chronic diseases. It is based on the philosophy of Yin and Yang theory, Five Element theory, Zang-Fu theory, Jing-luo and Organ Clock theory. It is a medical protocol which focuses on correcting imbalances of energy in the body. From its inception in China more than 2,500 years ago, this form of treatment is used traditionally to prevent, diagnose and treat disease, as well as to improve general health.
Acupuncture points are seen as places where nerves, muscles, and connective tissues can be stimulated. The stimulation increases blood flow, while at the same time triggering the activity of the body’s natural painkillers. In 2003, the World Health Organization (WHO) listed a number of conditions in which acupuncture has been found to be effective. These include high and low blood pressure, chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting, some gastric conditions, including peptic ulcers, painful menstruation, dysentery, allergic rhinitis, facial pain, morning sickness, rheumatoid arthritis, sprains, tennis elbow, sciatica, dental pain, reducing the risk of stroke, inducing labor.
All types of disorders are treated by influencing the appropriate meridian points. It is also used as anesthesia in surgical procedure. It has small branches which includes auriculotherapy and scalp acupuncture. Scalp acupuncture is a modern acupuncture technique in which needles are penetrated in the specific areas of the scalp or lines on the scalp. Scalp acupuncture has integrated Chinese needling methods with western medical knowledge of representative areas of the cerebral cortex.
- Cupping Therapy
- Moxibustion
- Auricular acupuncture
- Pulse diagnosis
- Deng H, Shen X. The mechanism of moxibustion: ancient theory and modern research. Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2013;2013.
- Gao De. A discussion on selected topics relating to pulse-taking diagnostics. Journal of the American College of Traditional Chinese Medicine. 1987; (1); 57-61.